Sheet Molding Compound (SMC)
• SMC is the paste that is compression molded
• 33% polyester resin and stryrene, which polymerizes and crosslinks
• 33% glass fibers (1” fibers)
• 33% Calcium Carbonate
Definition: A fiber glass reinforced thermosetting compound in sheet form, usually rolled into coils interleaved with plastic film to prevent autoadhesion. Made by dispensing mixed resin, fillers, maturation agent, catalyst and mold release agent onto two moving sheets of polyethylene film. The lower one also contains chopped glass roving or glass mat. SMC can be molded into complex shapes with little scrap.
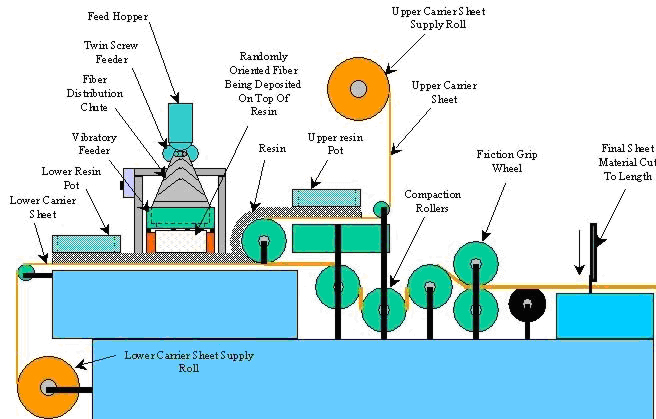 Sheet Molding Compound
Sheet Molding Compound:
Sheet molding compound (SMC) is fiberglass reinforced composite material, produced in a “sheet” format.
The process begins when continuous strand fiberglass (also called a “roving”) is chopped into desired lengths (usually under 2”). The strands are deposited onto a bottom layer of paste made from resin and filler. The paste and fiberglass strand travel through the processing machine, on a carrier film. A top layer of resin and filler paste sandwiches the fibers to the bottom layer of paste, and is covered by a top layer of carrier film. The “fiber and paste sandwich” is then compacted by a series of rollers to make a continuous sheet of molding compound.
SMC is made of 3 basic components: the base resign system (polyester, vinylester, epoxy, phenolic or polyimide), the reinforcements (fiberglass, graphite, aramide), and additives which include inert fillers, pigments, UV stabilizers, catalysts, inhibitors, and thickeners.
While there is basically no limit to the number and types of formulations that can be produced, it is important to prioritize the desired properties for the product. This helps to ensure that the optimum material system is achieved within the economic guidelines of the program.
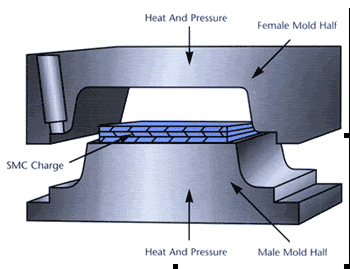 Description: Sheet Molding Compound (SMC)
Description: Sheet Molding Compound (SMC):
Sheet molding compound (SMC) consists of a doughy material composed of chopped glass fiber rovings, 0.75-2” in length, fillers (e.g. calcium carbonate, low profile additives, catalyst, catalyst aids, and a thermoset resin, normally a polyester based thermoset, epoxy or vinyl ester resin. The long fibers present in this material provide good stiffness and impact resistance. The initial paste has a viscosity near the 40,000-100,000 cps range. SMC is then packaged and placed into storage for 1 to 2 days allowing the resin to advance to achieve viscosities in the range of 60,000 to 750,000 poise. The thickening during this time period is usually assisted with additives like magnesium oxide, magnesium hydroxide, or calcium hydroxide. The aged SMC is then weighed, and placed into a heated compression mold (250-350oF) which under pressure (500-2500 psi) forms a composite part. Typical compression molding cycle times of 30 seconds to several minutes are possible with thicker parts requiring more dwell/curing time.
Overview of
SMC moulds Applications:
Cars and Trucks
SMC mould Series: Shock absorbers, oil troughs, cylinder head covers, engine bonnets, luggage boot lids, casings of the engine compartment, protective layers against stones...
General: House connection boxes, cable distribution boxes, interior linings, window frames, safety cut-outs, LS-switches, exterior linings, sliding valves, insulating plates, call boxes, ground plates of recycling containers, casings for industrial vacuum cleaners.

